© 2015 by AE 390 Students. Proudly created with Wix.com

Unlike usual heat pumps, the geothermal heat pump uses the earth (actually from the sun) as its own heat pump during the winter, but uses a heat sink for summer. This heat pump would be considered energy efficient as it is literally buried in your backyard. Given the cost and maintenance around energy sources like oil or fossil fuels, using geothermal heat pumps can save up to 30% on cost efficiency.
Geothermal Heat Pump
How it Works
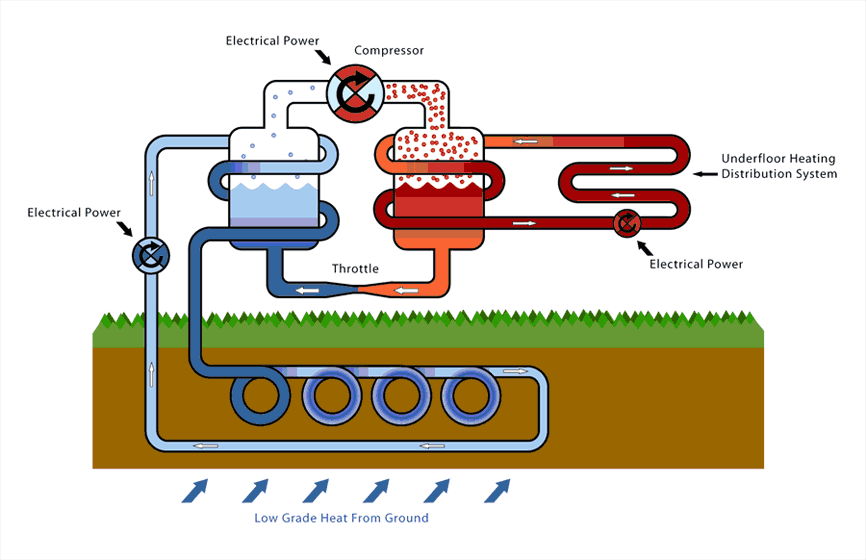
The geothermal heat pump is not much different than a standard heat pump if you enter someone’s residence. However, the key difference between the two is that there is no exterior HVAC system or some sort of outdoor compressor. The one thing people should always know about the geothermal heat pump is the loop. There are two basic loop systems: closed- loop and opened-loop. All of these loop systems are designed based on different factors, such as climate, soil conditions, amount of land, etc.
The heat pump simply moves heat energy from one place to another. Using refrigeration, the GHP removes the heat energy stored in the earth and transfers the energy to your home/building.
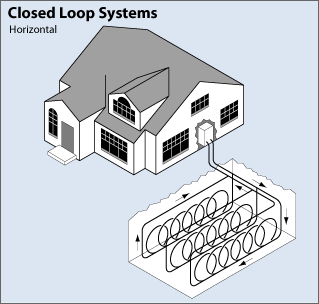
Closed-Loop System
Horizontal
This system is mostly cost-effective for residences, especially for new construction where the foundation below is not disturbed frequently. The system consists of two pipes, one buried to the ground at four feet and the other at six feet. Then the “Slinky” method was applied, by looping the pipes, allowing more pipe to flow in through the small trench, which can also cut down on installation cost for drilling the trench.
Horizontal (Pond/Lake)
The closed-loop system, horizontally affiliated with a pond or lake, may be the lowest cost option for a geothermal heat pump. It consists of a line pipe that runs underground from the building to the subsurface, coiled into big circle loops. The pipes have to be at least eight feet under the surface of the pond/lake, otherwise, the system will subject to freezing. However, in order for this installation to be successful, the water source must have the appropriate volume, depth, and other important factors.
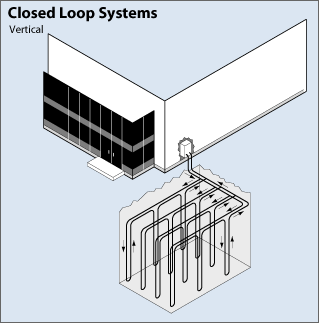
Vertical
The vertical closed-loop system are usually preferable in larger buildings like commercial and schools, mainly because of the huge amount of land required, which will limit the space for the trench, therefore, force to a vertical loop instead of a horizontal loop. Also on another note, if the soil is too shallow for adding trenches, they need to avoid the disturbance of the foundation, otherwise, the whole area will be then unsafe for construction. Therefore, they would have to add a vertical loop system to minimize any damage. Holes are drilled at about twenty feet apart and 100 to 400 feet deep. Two pipes are inserted into the holes and connect at the bottom to form a U-shape bend and eventually form into a loop. Then all the vertical loops are connected with a horizontal pipe, all connected to the pump in the building.
Open-Loop Systems
This system uses a surface body water, using it as the heat exchanger, making it circulate throughout the entire geothermal heat pump system. Once circulation is complete, the fluid returns to the ground and through the recharge well. This system can be very efficient if the water supply has adequate clean water.
Benefits
Low-Cost
Geothermal Heat pumps can supplement the home’s water heater, saving up to 30% hot water cost every year. Geothermal heat pumps also generate very little electricity, mainly for operations control, to transfer heat to and from the ground. Typically, homeowners save up to 30% to 70% in savings in electricity compared to regular HVAC systems.
Free Hot Water
Heat is removed from one;s home during the cooling cycle, and is directly deposited to the water heater instead of the ground. This is done by a simple connection made so the geothermal system can deliver hot water and be stored in the hot water heater. So technically speaking, this will provide you with free water.
Life Span
For ordinary HVAC systems, they require constant maintenance. GHP systems require little to no maintenance other than filter changes. All geothermal heat pumps are located indoors, taking out climate change and weather out of the equation. If properly maintained, geothermal heat pumps can last up to 20 years without any dilemmas.
Typical Uses
As for any heat pump, including geothermal, can heat, cool, and supply hot water if equipped by a residence. They can even replace a normal air-source unit of the same heating and cooling capacity, but can return the cost in 5 to 10 years.
Other uses for geothermal energy is heating of farms. Framers would use the water heated by the geothermal energy to grow vegetables and other consumables during the harsh winters. With this energy efficient unit, productivity does not have to slow down, and the economy will not have to worry about food shortage during the icy weather. Geothermal energy is also used in fish farms, where the controlled water to grow a range of animals, including various types of fish, catfish, flounder, reptiles, etc. For geothermal space heating, the farms would construct the closed loop system for anti-freeze through the ground where it would accumulate the natural heat of 50 F. Then the heat exchanger would transfer it to heated liquid and circulate the entire structure. They would also construct an opened loop system if there is an underground water source.
Geothermal energy can also be used industry-wise, especially for consumables. It can vary between drying of fruits, vegetables, wood, etc. It can vary between drying of fruits, vegetables, wood, etc. Usually industries in big buildings in more urban areas would use vertical loop systems, only because of the limited spacing.
Limitations
The benefits of geothermal heat pumps can definitely persuade one consumer to replace their old HVAC system and replace with geothermal energy. However, there can be still some challenges the system faces. The geothermal systems have a very high initial cost, so even though the payback period makes the geothermal energy option a “no-brainer”, it may take a little while to accumulate the necessary resources to obtain it. Also on a side note, energy-saving technology isn’t valued by the lenders. The mortgage lending companies are not familiar with geothermal energy and what its payback periods represent, therefore, it may be even more difficult to obtain a loan for the geothermal heat pump.
This minor concern is rapidly evaporating, but geothermal heat pump installation requires highly trained personnel. This mostly cannot be done by a normal HVAC technician. The person would have to have wide range of engineering skills, including thermodynamics, geotechnical engineering, mechanical engineering, and hydraulics. Also, steam may run out over a period of time due to temperature drop, which can lead to huge loss invested by the consumer. So the technician would have to do extensive initial research before setting up for the installation.
Since geothermal energy functions with natural chemical gases, some geothermal sites contain high levels of poisonous gases. If those gases are released accidently, it can cause an epidemic, which is why the geothermal plant must be able to contain these harmful hazards, as they can easily escape through the holes drilled by the construction workers.
Numeric Parameters
This graph represents the Annual Carbon This bar graph represents the annual cost
Dioxide Emissions from Space Conditioning. for each alternative heating system. As
As shown, GHP systems have the least annual shown, geothermal heat pumps are the
cost comapring to other alternatives in least spending option, about $242 less
various ppopulated areas in the United than Air Source Heat Pump.
States.